Introduction
A. Definition of the era
Technology has been instrumental in revolutionizing diverse industries, and the medical field is no exception. In this weblog, we can explore 5 cutting-edge technologies which are enhancing healthcare in terrific ways. These technologies include Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), Telemedicine, Blockchain, and 3-D Printing. Each of these technologies brings specific benefits and transformative capacity to the clinical area.
B. Importance of era inside the medical area
The integration of the era in healthcare has the power to enhance patient effects, beautify performance, and power innovation. By leveraging advanced technology, healthcare professionals could make more correct diagnoses, provide customized treatment plans, and offer far-off medical offerings. Additionally, generation facilitates the steady alternate of clinical information, streamlines healthcare approaches, and permits the creation of customized scientific devices. These advancements now not best benefit sufferers but additionally empower healthcare providers to deliver incredible care.
C. Overview of the blog structure
This blog will delve into every of the 5 technology and their impact in the medical area. We will explore their programs, advantages, and potential challenges. The following sections will provide an in-depth evaluation of each generation
Technology 1: Artificial Intelligence (AI)
A. Explanation of AI in healthcare
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of laptop technology that focuses on creating intelligent machines capable of appearing responsibilities that normally require human intelligence. In the context of healthcare, AI involves the development of algorithms and structures that can analyze scientific statistics, interpret photos, and make informed decisions.
AI in healthcare utilizes gadgets gaining knowledge of algorithms and deep neural networks to system big quantities of clinical information, which includes patient facts, clinical pictures, and studies findings. These algorithms can pick out patterns, apprehend anomalies, and generate treasured insights that aid in analysis, treatment-making plans, and decision-making.
B. Applications of AI in scientific diagnostics
One of the huge contributions of AI in healthcare is its software in scientific diagnostics. AI algorithms can examine medical pictures such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs with first-rate accuracy. By training on significant datasets, AI systems can come across subtle abnormalities that are probably overlooked by human radiologists. This enhances the speed and accuracy of analysis, main to early detection of diseases like cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and neurological issues.
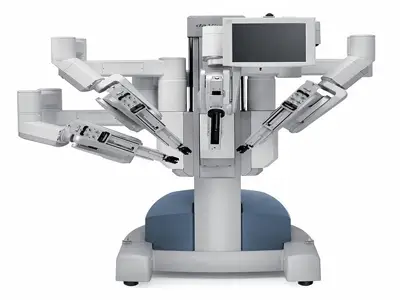
C. AI-assisted robotic surgical procedures
AI has additionally paved the way for sizable improvements in surgical tactics through AI-assisted robotic surgical procedures. Surgeons can utilize robotic systems ready with AI algorithms to carry out specific and minimally invasive surgeries. These robots can offer more advantageous visualization, dexterity, and balance, lowering the hazard of complications and improving affected person results. AI algorithms can assist surgeons by reading actual-time facts for the duration of the operation, supplying guidance, and even automating certain obligations.
D. Enhanced affected person care and customized remedy plans
AI allows healthcare vendors to deliver personalized care and remedy plans tailored to each affected person’s precise wishes. By analyzing the affected person’s information, along with scientific history, genetic facts, lifestyle elements, and remedy effects, AI algorithms can discover styles and correlations that resource in predicting disorder progression, deciding on the simplest remedy alternatives, and optimizing medication dosages. This level of personalization complements affected person care, will increase remedy fulfillment charges, and decreases negative results.
E. Potential demanding situations and moral considerations
While AI gives super capability in healthcare, it also increases sure challenges and moral concerns. One difficulty is the reliability and interpretability of AI algorithms. As AI systems grow to be increasingly complex, it may be difficult to recognize how they come at their decisions. Ensuring transparency and accountability in AI algorithms is essential to preserve agree with and validate their results.
Data privacy and safety are extra concerns when using AI in healthcare. Patient records are enormously sensitive and need to be safeguarded against unauthorized access or breaches. Adhering to strict information protection rules and imposing strong cybersecurity measures is crucial to deal with those worries.
Moreover, there are moral considerations surrounding the usage of AI in affected person care. For example, the ability for bias in AI algorithms and its impact on healthcare disparities have to be carefully addressed. AI structures need to learn on various and consultant datasets to ensure fairness and equitable effects for all affected person populations.
In conclusion, AI can revolutionize healthcare by using improving diagnostics, enabling AI-assisted surgeries, enhancing personalized remedy plans, and optimizing patient care. However, it is vital to navigate the challenges and ethical considerations associated with AI to make sure its accountable and beneficial integration into the clinical field.
Technology 2: Internet of Things (IoT)
A. Understanding IoT in healthcare
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected gadgets that could gather, alternate, and analyze facts via the net. In the context of healthcare, IoT involves connecting clinical gadgets, wearables, and sensors to a community, permitting the seamless transmission and analysis of affected person information. This technology revolutionizes healthcare by way of enabling real-time monitoring, records-pushed choice-making, and improved affected person effects.
B. Benefits of IoT in faraway patient monitoring
One of the important thing benefits of IoT in healthcare is far-flung patient tracking. IoT gadgets can monitor essential signs, which include heart price, blood pressure, glucose stages, and oxygen saturation, in real-time. These records can be transmitted to healthcare carriers, permitting them to monitor sufferers’ health remotely and interfere proactively whilst essential. Remote affected person monitoring reduces the need for frequent health center visits, improves patient comfort, and permits early detection of deteriorating situations, leading to well-timed interventions.
C. Improved clinical device integration and statistics collection
IoT enables the mixing of various clinical devices, creating a unified and interconnected healthcare ecosystem. Medical devices, including infusion pumps, pacemakers, and glucose monitors, may be connected to a community, enabling seamless records series and transmission. This integration streamlines healthcare workflows, removes manual facts entry mistakes, and presents complete and updated affected person statistics. Healthcare experts can get the right of entry to real-time records, improving their capacity to make informed decisions and deliver well-timed interventions.
D. Enhanced healthcare analytics and predictive modeling
IoT-generated facts fuel healthcare analytics and predictive modeling. By gathering sizeable amounts of real-time data, IoT devices make contributions to deeper expertise of affected persons’ health tendencies, ailment patterns, and remedy effects. Advanced analytics algorithms can leverage these records to become aware of correlations, predict ailment development, and optimize treatment strategies. Predictive modeling enables proactive interventions, customized medicine, and greater efficient allocation of healthcare sources, in the long run improving patient results and lowering charges.
E. Security and privateness worries with IoT in healthcare
While IoT brings several benefits to healthcare, it also raises issues concerning security and privacy. The increased connectivity and facts exchange introduce vulnerabilities that can be exploited by using cybercriminals. Safeguarding affected person information from unauthorized get right of entry, making sure facts are integrity, and enforcing sturdy encryption and authentication mechanisms are important to mitigate those risks.
Furthermore, IoT gadgets may capture touchy affected person records, elevating privacy worries. It is important to conform to data safety guidelines, attain patient consent, and make certain steady records storage and transmission. Striking the right stability between statistics accessibility and privacy protection is critical for keeping affected persons agree with and upholding ethical requirements.
In the end, IoT offers notable ability in healthcare, enabling faraway patient tracking, seamless integration of scientific devices, superior analytics, and predictive modeling. However, it is vital to coping with security and privacy worries to make sure the responsible and steady implementation of IoT in healthcare settings. By doing so, we can harness the overall energy of IoT to beautify patient care, enhance results, and pressure innovation in the clinical subject.
Technology three: Telemedicine
A. Defining telemedicine and its significance
Telemedicine refers to the transport of healthcare services and consultations remotely, the usage of telecommunications generation. It lets healthcare vendors engage with patients thru video calls, telephone calls, or online messaging platforms. Telemedicine has gained extensive significance in cutting-edge healthcare because it breaks down geographical limitations, improves access to care, and enhances patient-provider conversation.
B. Remote consultations and virtual healthcare services
One of the important thing programs of telemedicine is remote consultations and digital healthcare offerings. Patients can hook up with healthcare specialists from the comfort of their houses, eliminating the need for in-individual visits for non-emergency situations. Through video or audio calls, medical doctors can investigate signs, offer clinical advice, prescribe medications, and even monitor persistent conditions. Virtual healthcare services encompass a wide variety of specialties, which includes number one care, intellectual fitness, dermatology, and compliance with-up visits.
C. Accessibility and comfort for sufferers in faraway regions
Telemedicine addresses the undertaking of healthcare accessibility, mainly for patients living in faraway or underserved areas. It permits individuals to discuss with experts who may be positioned some distance away, doing away with the want for a lengthy-distance tour and associated fees. This era bridges the distance between patients and healthcare companies, making sure that even those in remote regions have to get entry to the best healthcare offerings. Additionally, telemedicine improves healthcare access for people with mobility obstacles or transportation boundaries.
D. Reducing healthcare costs and health facility overcrowding
Telemedicine offers substantial fee-saving possibilities for both patients and healthcare structures. By decreasing the want for in-individual visits, telemedicine eliminates transportation fees, time off from work, and different expenses associated with conventional healthcare appointments. Moreover, it can help alleviate the load on hospitals and clinics by diverting non-urgent cases to far-off consultations, reducing overcrowding in healthcare centers. Telemedicine also lowers healthcare prices with the aid of preventing useless emergency room visits and clinic admissions thru early intervention and faraway monitoring.
E. Legal and regulatory considerations for telemedicine
The adoption of telemedicine includes navigating criminal and regulatory considerations. Healthcare carriers and organizations need to follow local, country, and countrywide guidelines concerning telemedicine practice, privateness, and reimbursement. Licensing requirements for healthcare specialists supplying telemedicine services across the nation or country-wide borders must be considered. Additionally, ensuring the security and privacy of affected person facts in the course of telemedicine interactions is important, requiring compliance with data protection guidelines and enforcing robust cybersecurity measures.
In conclusion, telemedicine is remodeling the healthcare landscape using permitting far-flung consultations, improving accessibility, lowering costs, and addressing overcrowding in healthcare centers. While it gives several benefits, healthcare vendors and agencies should navigate prison and regulatory issues to make sure compliance and patient information protection. With the ongoing improvements in telemedicine generation and regulatory frameworks, the ability for far-flung healthcare delivery will preserve to enlarge, enhancing affected person care and improving healthcare outcomes.
Technology 4: Blockchain
A. Introduction to the Blockchain era
Blockchain is a decentralized and allotted ledger technology that allows for steady and transparent recording of transactions across a couple of computer systems or nodes. It operates in a community in which each transaction is saved in a “block” connected to previous transactions, forming a chain of blocks. Blockchain technology offers immutability, transparency, and agree with in facts control, making it a progressive answer with capability programs in the healthcare enterprise.
B. Securing scientific statistics and patient facts
One of the significant applications of blockchain in healthcare is securing scientific facts and affected person statistics. Traditional healthcare systems often face demanding situations associated with facts breaches and unauthorized get entry to touchy patient information. By leveraging blockchain, patient facts may be encrypted and stored in a decentralized way, with each transaction securely recorded and connected. This complements statistics security, reduces the threat of tampering or unauthorized get admission, and gives patients more manipulation over their fitness facts.
C. Streamlining healthcare information alternative and interoperability
Healthcare records trade and interoperability are crucial for delivering coordinated and efficient care. However, the contemporary healthcare machine regularly faces interoperability-demanding situations because of disparate structures and siloed facts. Blockchain generation can facilitate seamless and stable statistics sharing amongst distinct healthcare providers, payers, and stakeholders. By setting up a standardized and transparent platform for information exchange, blockchain complements interoperability, streamlines care coordination and improves affected person results.
D. Tracking pharmaceutical delivery chains and reducing counterfeit pills
Counterfeit tablets pose giant dangers to patient safety and public health. Blockchain technology gives a potential solution by allowing the monitoring and verification of pharmaceutical supply chains. By recording each transaction from the point of foundation to the point of shipping at the blockchain, stakeholders can make certain of the authenticity and integrity of medicinal drugs. This complements drug safety, reduces the circulation of counterfeit capsules, and improves traceability in case of remembers or destructive activities.
E. Addressing privacy worries and ability boundaries
While blockchain technology offers promising answers in healthcare, it also gives challenges and capability barriers. Privacy worries get up because of the everlasting and obvious nature of blockchain transactions. Ensuring patient privacy and complying with data safety rules require careful implementation, together with encrypting touchy statistics and presenting sufferers with control over their facts through consent mechanisms.
Additionally, scalability and strength consumption are concerns for blockchain adoption. As the variety of transactions will increase, blockchain networks may additionally face scalability problems, main to slower transaction speeds and higher costs. Energy intake in blockchain networks, specifically in evidence-of-work-based totally systems, has raised environmental issues that want to be addressed via more power-efficient consensus mechanisms.
In the end, the blockchain era can revolutionize healthcare using securing clinical information, streamlining data trade, and addressing pharmaceutical delivery chain demanding situations. However, cautious consideration of privacy, scalability, and power intake is essential for its successful implementation. As blockchain keeps evolving, collaboration among stakeholders, ongoing research, and regulatory frameworks can be important in harnessing its complete potential for the advantage of the healthcare industry and affected person care.
Technology five: three-D Printing
A. Overview of 3D printing in healthcare
3-d printing, also referred to as additive manufacturing, is a technology that constructs physical items layer by layer based on a virtual model. In healthcare, 3-D printing has emerged as an effective device, enabling the manufacturing of custom-designed scientific gadgets, tissues, and organs. It gives several benefits which include quicker manufacturing, feed efficiency, and design flexibility, revolutionizing the manner healthcare carriers approach patient care.
B. Customized medical devices and prosthetics
One of the significant programs of three-D printing in healthcare is the production of custom-designed scientific devices and prosthetics. Traditional manufacturing strategies often result in well-known, one-length-fits-all devices. With 3D printing, healthcare companies can create customized clinical devices tailor-made to every patient’s unique anatomy and desires. This era lets in for the ideal design and fabrication of prosthetics, implants, orthotics, and surgical gadgets, leading to advanced patient comfort, capability, and consequences.
Organ and tissue printing for transplantation
3-d printing holds brilliant promise in the discipline of regenerative medicine by using enabling the fabrication of organs and tissues for transplantation. Scientists and researchers are exploring the usage of bio-inks, which might be biocompatible substances containing residing cells, to print complicated structures like blood vessels, heart tissue, pores, and skin grafts. Although the development of fully functional organs continues to be in its early stages, three-D printing gives hope for addressing the organ scarcity crisis and offering personalized organ replacements in the future.

D. Rapid prototyping for scientific research and education
three-D printing serves as a valuable tool for fast prototyping in scientific studies and education. Researchers can create anatomically accurate fashions of organs, bones, and complicated anatomical structures for surgical making plans, education, and schooling functions. Surgeons can exercise elaborate processes on 3D-published replicas, enhancing their abilities and decreasing the hazard of mistakes for the duration of real surgical procedures. Furthermore, 3-D printed models useful resources in scientific tool improvement, allowing for iterative layout upgrades and trying out earlier than mass production.
E. Regulatory challenges and future opportunities of 3-D printing
The adoption of 3D printing in healthcare faces regulatory challenges and issues. As the era evolves, regulatory bodies want to set up hints and requirements to make sure the protection, efficacy, and pleasantness of 3-D-published clinical devices and fabricated tissues. Additionally, issues related to intellectual assets, legal responsibility, and compensation models require cautious interest to encourage innovation and good-sized adoption.
Looking to the future, 3-d printing holds the immense ability for advancing customized medicinal drugs and reworking affected person care. As the era improves, the variety of printable materials will enlarge, enabling the introduction of more complicated systems and purposeful tissues. In addition to improvements, 3-d printing may additionally play a vital function in on-demand organ printing, regenerating broken tissues, and advancing drug delivery systems. Continued studies, collaboration among stakeholders, and regulatory frameworks will form the future possibilities of three-D printing in healthcare.
In the end, 3-d printing is revolutionizing healthcare via permitting the production of custom-designed medical gadgets, tissue engineering for transplantation, speedy prototyping, and medical education. While regulatory challenges exist, the future potential of three-D printing in advancing customized medicine and enhancing affected person consequences is promising. Embracing this transformative technology can pave the manner for groundbreaking improvements and form the future of healthcare.
Conclusion
A. Recap of the mentioned technologies
In this weblog, we explored 5 transformative technology which might be revolutionizing the clinical field. We discussed Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its applications in clinical diagnostics, robotic surgeries, and personalized treatment plans. The Internet of Things (IoT) was highlighted for its benefits in remote affected person tracking, scientific tool integration, and healthcare analytics. Telemedicine become tested for its role in faraway consultations, progressed accessibility, and value reduction. The blockchain era changed into exploring for securing clinical facts, streamlining information change, and tracking pharmaceutical supply chains. Lastly, three-D printing become mentioned for its customization of medical gadgets, organ and tissue printing, and rapid prototyping.
B. The transformative effect of generation on healthcare
The effect of this technology on healthcare has been transformative. They have stepped forward to affected person consequences, enhanced accessibility, reduced costs, and streamlined healthcare strategies. AI has revolutionized diagnostics and treatment planning, leading to extra correct and customized care. IoT has enabled faraway tracking and better integration of scientific gadgets, ensuing in proactive and green healthcare delivery. Telemedicine has damaged geographical boundaries, bringing pleasant healthcare to far-off areas and decreasing hospital overcrowding. Blockchain technology has better statistics security, supply chain control, and affected person privacy. 3-d printing has opened new possibilities for customized medical gadgets, tissue engineering, and scientific education.
C. Anticipated destiny developments and demanding situations
Looking to destiny, this technology will continue to conform and result in additional advancements in healthcare. AI turns into extra sophisticated, assisting in complex choice-making and riding precision remedy. IoT will extend its reach, permitting the seamless integration of diverse healthcare systems and devices. Telemedicine will see progressed functionalities, including digital reality applications and far-off surgeries. Blockchain will deal with regulatory demanding situations, making sure of privacy and interoperability throughout healthcare networks. Three-D printing will advance organ transplantation, regenerative medicine, and drug transport systems.
However, those advancements additionally come with challenges. Ethical issues, records privacy, safety, and regulatory frameworks want to be addressed. Integration of this technology into current healthcare structures and attractiveness with the aid of healthcare professionals and patients requires careful planning and training. Continuous research and collaboration between era specialists, healthcare companies, and policymakers may be critical in overcoming those challenges.
D. Encouragement for embracing the era of a higher healthcare system
In conclusion, embracing these transformative technologies is critical for building a higher healthcare system. The ability to decorate patient care, enhance outcomes, and force innovation is huge. Healthcare providers, policymakers, and stakeholders ought to actively embrace and adopt these technologies, making sure ethical implementation, regulatory compliance, and privacy protection. By leveraging AI, IoT, telemedicine, blockchain, and 3-d printing, we can create a healthcare environment that is greater handy, personalized, and efficient.
The destiny of healthcare lies in the collaboration between human knowledge and technological advancements. Let us capture the opportunities offered by these technologies, triumph over the demanding situations, and paintings towards a healthcare gadget that is pushed with the aid of innovation, compassion, and advanced-affected person well-being. Together, we can form the destiny of healthcare and create a more fit world for all.